Lung Cancer
Introduction
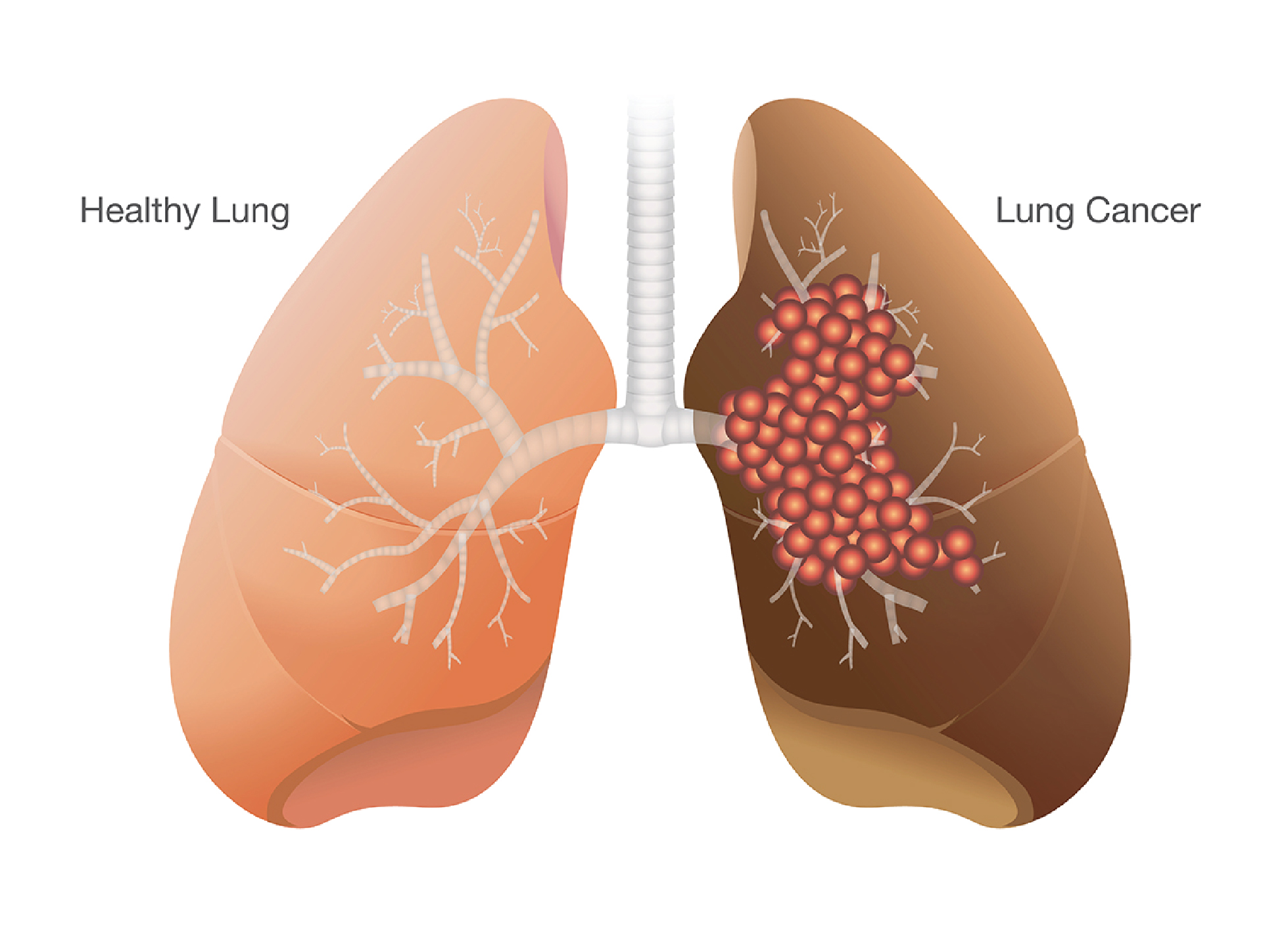
Lung cancer accounts for 13 per cent of all new cancer cases and 19 per cent of cancer related deaths worldwide. Lung cancer is a form of cancer that starts in the lungs and reducesthe ability to breathe. It can spread to other part of the body in later stage. The first place were lung cancer spread is the lymph node in the center of the chest. In the later stages, lung cancer can spreads to distant part of the body, such as liver, brain or bones.
Risk factor
There are various risk factors associated with lung cancer that is further categorised as modifiable (risk factors you can change) and non-modifiable (risk factors you can't change).
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is divided into two types :
Signs & Symptoms

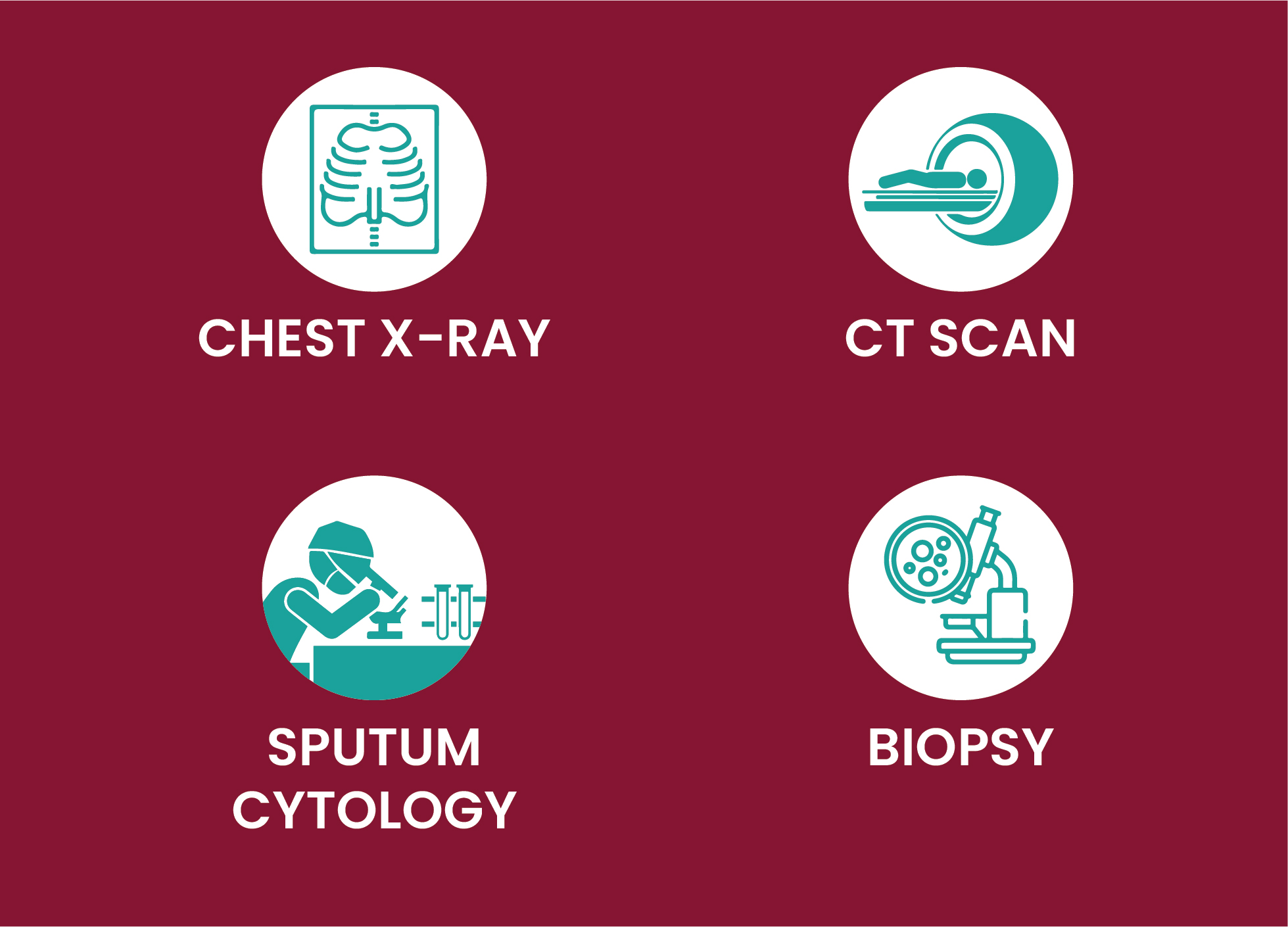
Diagnosis
Management
The main goal of treatment is to manage symptoms and keep them under control for as long as possible. The doctor may advise the cancer treatment plans based on several factors, such as overall health, the type, the stage of cancer and the size of cells present, and whether they have spread. Often, combinations of therapies are used.Lung cancer treatment includes surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stereotactic body radiotherapy, targeted drug therapy, and immunotherapy.
Quitting smoking after a diagnosis of early-stage lung cancer may also help to manage people to live longer, a recent study found that quitting smoking could delay a return of cancer or worsening of the disease.
Follow-Up
Your healthcare expert will help you understand what to expect after cancer treatment in terms of follow-up, lifestyle changes, and making important health-related decisions.
