Lymphoma Cancer Specialist in Delhi
Introduction
Cancer developing in the lymphatic system and various parts of the lymph glands are called Lymphoma. Lymphoma is the sixth most common cancer in all types of cancer. It damages the abdomen, throat, esophagus and causes chest pain. Thus, it can be dangerous and needs immediate medical attention.
Cancer affecting the Lymphatic System/ lymph nodes of the body is known as Lymphoma. It is a type of blood cancer in which the cancer-causing abnormal cells target the bone marrow where they infect the lymphocytes. Lymphoma cancer specialist in Delhi concur that it weakens the immune system of the human body because of the depleting number of white blood cells in the human body.
Types of Lymphoma
The two main types of lymphoma are:
Causes of Lymphoma
Cancer is the result of uncontrolled cell growth. The average lifespan of a cell is brief, and then the cell dies. In people with lymphoma, however, the cell thrives and spreads instead of dying. It's unclear what causes lymphoma, but lymphoma cancer specialists agree that several risk factors are connected with these cancers.
Risk Factor of Lymphoma
Factors that can increase the risk of lymphoma include:
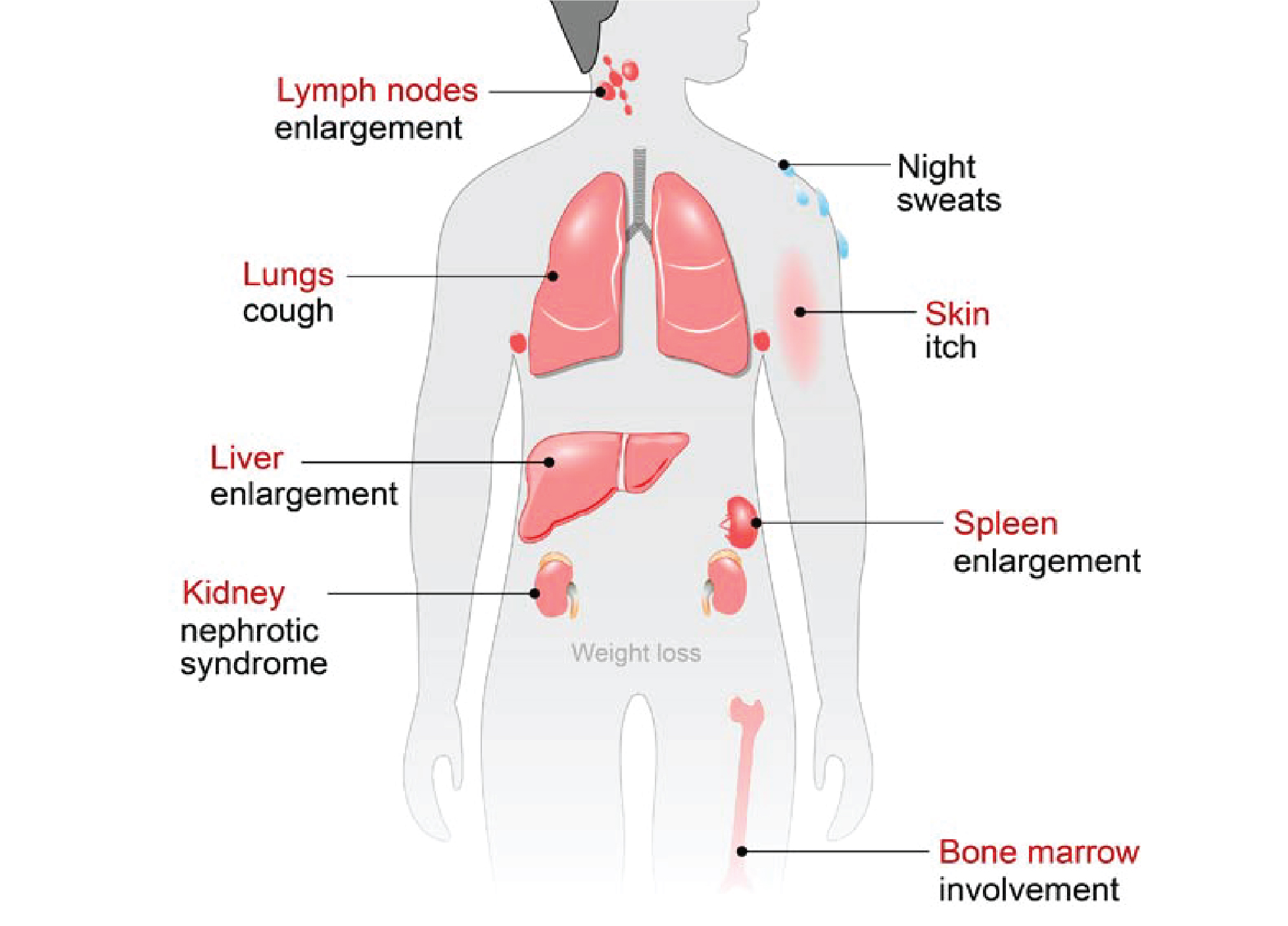
Symptoms of Lymphoma
The symptoms of both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas are:
Lymphoma Diagnosis
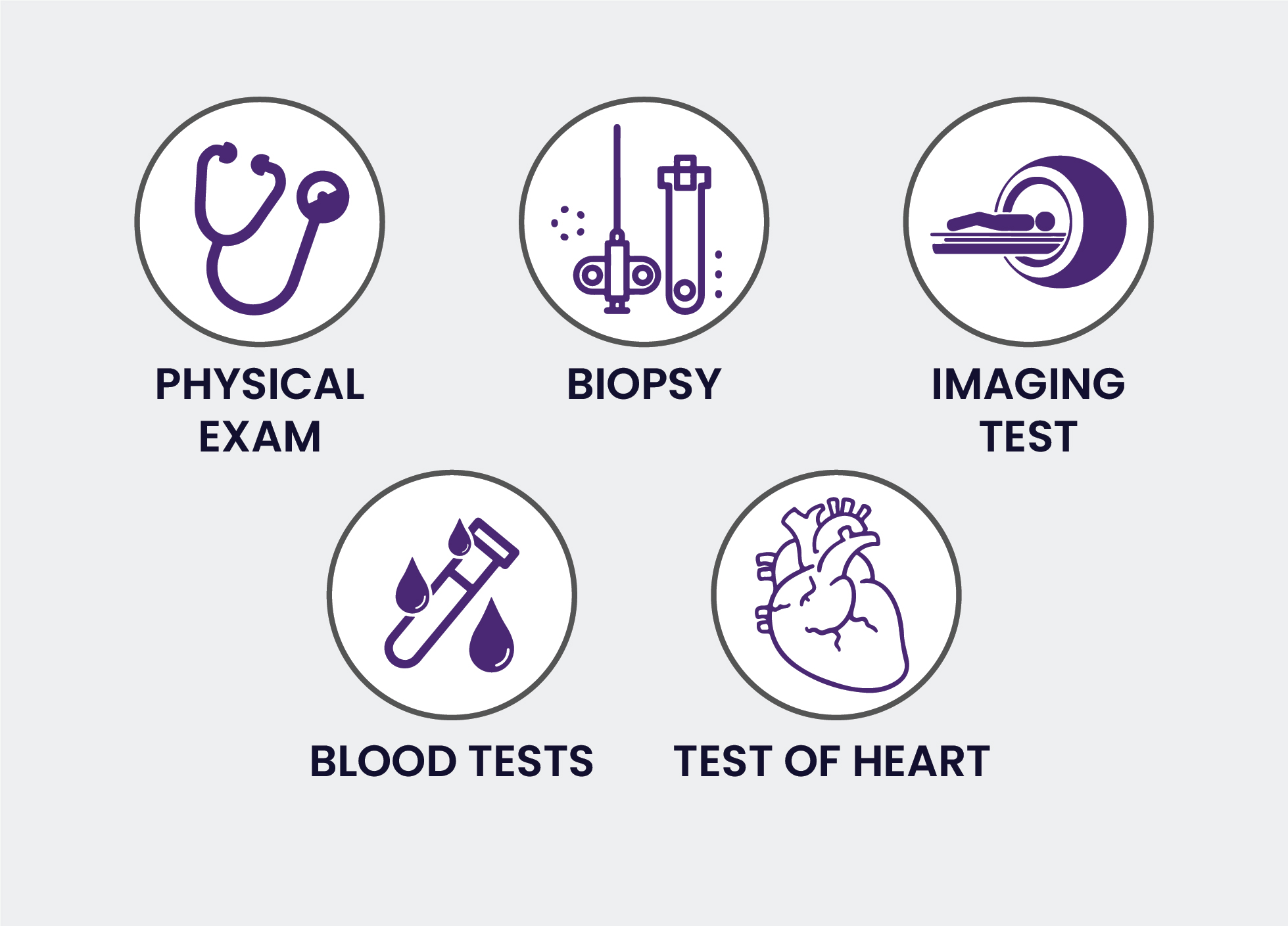
In the initial stage, lymphoma cancer reveals symptoms of Leukemia. Thus, people tend to get confused. Hence, the doctor will ask to run a few tests which are helpful to diagnose the condition:
The diagnosis includes:
These are some of the possible symptoms and are not always conclusive. You have to consult with a lymphoma cancer specialist in Delhi to ensure you are getting the proper diagnosis you actually need.
Lymphoma Treatment
There are various management options available for Lymphoma, and it is treatable too. Lymphoma cancer doctors in Delhi conclude about the treatment method according to the Detection test report.
Lymphoma Follow-Up
Most hospitals have follow-up appointments for around 2 years after finishing treatment for lymphoma, though some offer it for longer.
You usually need to have check-ups with your lymphoma cancer specialist every few months at first, then every 6 months. Having frequent appointments during this time means that your medical team can check for any signs of your lymphoma coming back- the risk of which is higher in the first 2 years after treatment.

